Design/Print Reference
How to supply documents and artwork to designers
- Submit your photographs in JPEG or TIFF format
- Logos need to be provided in EPS or high resolution JPEG format
- Provide captions for your photographs and clearly label them in any attachment and include names of any people in the photographs, if known
- Always supply copy / text as a Word document and ensure it is the final approved version before the designer formats it
- The person who submits the job request must ensure that the final document is signed off by their manager and other relevant stakeholders.
ISO A Series paper formats
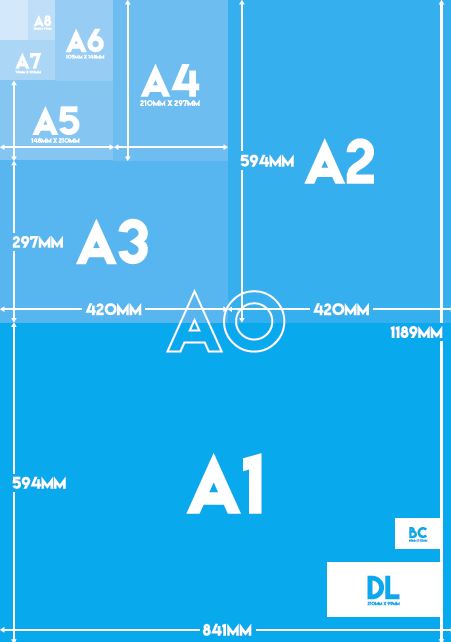
A0 841 x 1189mm
A1 594 x 841mm
A2 420 x 594 mm
A3 297 x 420mm
A4 210 x 297mm
A5 148 x 210mm
A6 105 x 148mm
A7 74 x 105mm
A8 52 x 74mm
A9 37 x 52mm
Design/ Print glossary
Bitmap A bitmap image is composed of a grid of dots (also called pixels). Digital photographs are bitmaps. Bitmap images cannot be easily scaled up in size without loss of quality.
Bleed When an image or design goes right to the edge of the printed sheet. The job is printed on oversize stock and the design extends about 3-5 mm beyond the intended page size. The bleed is then trimmed off in the finishing process.
Coated A smooth coated paper obtained by adding a coating of china clay compound on both sides of the paper. Coatings are normally defined as gloss, semi-gloss or matte surfaces.
Color proof A colour sample that attempts to represent the final design when printing is outsourced. Colour proofs can be generated from film separations before using them to make printing plates.
Duotone A black and white image reproduced using two halftone negatives and printed in black and one other colour ink.
Foiling/foil A letterpress based printing process that transfers a very thin layer of shiny metallic alloy onto the printed surface. Available in many different colours and patterns (including holographic) and used primarily to add a traditional or flamboyant element to a job’s design. Greeting cards are a good example of this printing application.
Four colour process This is the standard printing method that uses the four process colours of cyan (C), magenta (M), yellow (Y) and black (K). These four inks are combined in varying percentages to create a broader spectrum of colour.
JPG (or JPEG, Joint Photographic Experts Group) Standardised image compression format developed by the Joint Photographic Experts Group. Used for compressing full colour and grayscale images. The standard format for digital camera files.
Line art Single colour logos, drawings or diagrams that consist of only black and white without intermediate grayscale information. See also Bitmap.
LPI (lines per inch) The number of lines per inch on a halftone screen. As a general rule, the higher the LPI, the higher the printed resolution and quality.
Metal foil A mechanical process stamps the block under high pressure onto rolls of thin metallic foil which thus transfers the foil image onto the printed stock. It includes a variety of colours and finishes including matt, gloss and holographic.
Metallic inks Gold and silver semi-reflective inks used for special effects in print design. In most cases, it should be printed on coated gloss art or high gloss cast coated stock, or the ink may be absorbed into the stock and leave a dull finish.
Pantone Matching System (PMS) A system of colour that ensures repeatable mixing of specific spot colour inks no matter where or on what stock the job is printed. Typically a printer will show a customer a PMS book in order to choose a specific spot colour, identified by a number, which is to be used in their print job.
PDF (portable document format) A file format from Adobe that allows the distribution of digital files across any operating system or platform.
Perfect binding A common method of binding books. After the printed sections have been collated, the spines will be ground off and the cover glued on. The finished product is then trimmed flush with the cover.
Pixelated An undesirable effect caused by images or lines being rendered at too low a resolution.
PPI (pixels per inch) A measure of the density of scanned pixel information in an image. The finer the optics of the scanner, the higher the scan resolution.
Prepress The process of getting an image ready to go on press. Digital prepress denotes the entire preparation of a digital file for printing in either a digital or conventional system.
Process colour The process colours (cyan, magenta, yellow and black) are used in traditional colour printing to reproduce a full colour range.
Proof A laser printout or similar used to evaluate the typesetting and design of a job before printing. Some printers also use a digital PDF proofing process, which generally saves time and cost as the proof can be emailed.
Resolution The quality of a graphic file is measured by the number of pixels or dots per inch (DPI) the image contains. A high resolution file might typically be 300 DPI and is suitable for printing jobs. A 72 DPI the image is considered to be a low resolution image, only useful for website design.
RGB A colour model using red, green and blue – the additive primary colors. Computer monitors and televisions use RGB data to create screen images.
Saddle stitch A method of binding where the folded pages are stitched through the spine from the outside, using wire staples. Usually limited to about 64 pages.
Scoring Heavy card weight stock can get unsightly bumps when folded. To prevent this a score is made along the fold line using a scoring wheel on the printing press. A shallow indentation is thus made ensuring the item folds neatly.
Serif/sans-serif Refers to different styles of letter forms. Serif typefaces have the little hats and tails on the ends of the up and down strokes. Sans meaning typefaces don’t have the hats.
Spot colours These colours are printed as solid areas and used when fewer than four colours are needed or when the four colour process (CMYK) is unable to accurately reproduce a colour.
TIFF (or TIF) Stands for tagged image file format and is the preferred file format used for bitmap images in the graphics industry. The best format to use when you don’t want to lose quality in your image.
Tint A percentage of a solid ink. Tints are created to create the impression of a lighter colour when the ink is printed onto paper or another medium.
Zip To compress a file using WinZIP or similar compression software. Commonly used to reduce the size of a file and to group many files into a single archive, in order to speed transmission over the internet.